Investing in Fixed Assets: A Foundation for Growth and Stability
Related Articles: Investing in Fixed Assets: A Foundation for Growth and Stability
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Investing in Fixed Assets: A Foundation for Growth and Stability. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Investing in Fixed Assets: A Foundation for Growth and Stability

In the realm of finance, the concept of "fixed assets" often emerges as a cornerstone for long-term financial security and growth. These assets, characterized by their tangible nature and extended lifespan, represent a significant investment that can drive profitability and generate enduring value. Understanding the nuances of investing in fixed assets is crucial for individuals, businesses, and even governments seeking sustainable financial strategies.
Defining Fixed Assets: Tangible Pillars of Value
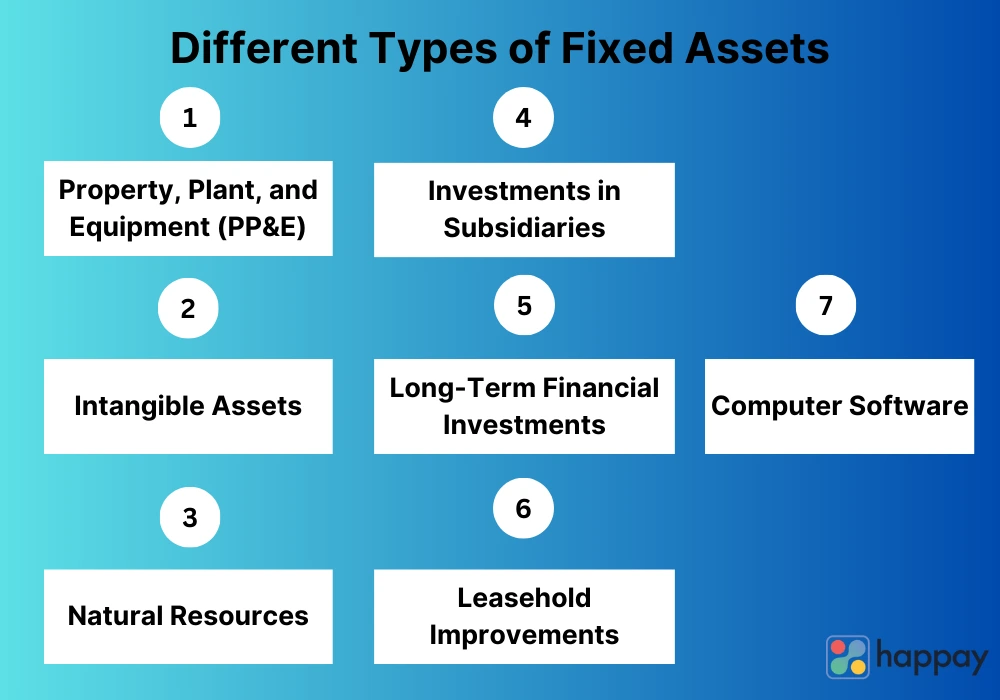
Fixed assets, often referred to as tangible assets, are physical resources that a company or individual owns and uses in its operations. They are typically characterized by their durability and longevity, providing a sustained benefit over an extended period. Common examples of fixed assets include:
- Real Estate: Land and buildings, both commercial and residential, represent a substantial investment with the potential for appreciation and rental income.
- Machinery and Equipment: Tools, vehicles, and other industrial equipment are vital for businesses to operate efficiently and generate products or services.
- Infrastructure: Roads, bridges, power grids, and other essential infrastructure projects are vital for economic development and societal well-being.
- Technology: Computers, servers, software, and other technological assets are crucial for businesses operating in the digital age.
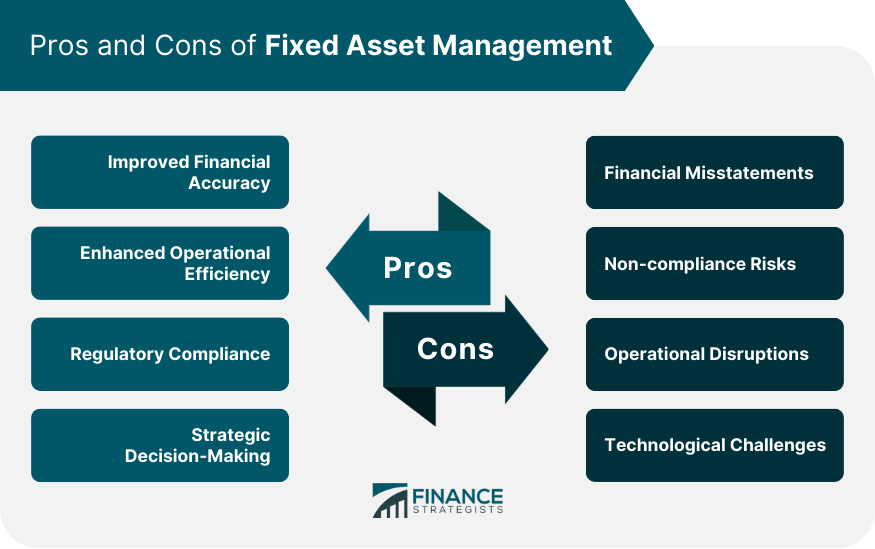
The Advantages of Investing in Fixed Assets:
Investing in fixed assets offers a range of advantages, making them an attractive component of a well-balanced portfolio:
- Stability and Security: Fixed assets provide a sense of stability and security, acting as a foundation for long-term financial planning. Their tangible nature and longevity offer a degree of protection against market volatility.
- Income Generation: Fixed assets can generate income through rental payments, lease agreements, or the sale of goods and services produced using the asset. This income stream contributes to financial stability and growth.
- Appreciation in Value: Over time, fixed assets can appreciate in value, particularly real estate. This appreciation can translate into substantial capital gains, further enhancing financial returns.
- Tax Benefits: In many jurisdictions, investing in fixed assets can provide tax benefits, such as depreciation deductions, which can reduce tax liabilities and improve profitability.
- Reduced Operating Costs: Investing in efficient machinery and equipment can lead to reduced operating costs, increasing productivity and profitability.
- Competitive Advantage: Investing in cutting-edge technology or modern infrastructure can provide a competitive advantage, allowing businesses to operate more efficiently and cater to evolving market demands.
Understanding the Risks and Considerations:
While investing in fixed assets offers numerous benefits, it’s crucial to acknowledge the associated risks and considerations:
- High Initial Investment: Fixed assets often require significant upfront capital investment, which can be a barrier for individuals and smaller businesses.
- Maintenance and Depreciation: Fixed assets require ongoing maintenance and repairs to ensure their functionality. Additionally, they depreciate over time, reducing their value.
- Market Fluctuations: The value of fixed assets can be influenced by market fluctuations, economic conditions, and other external factors, potentially impacting their profitability.
- Liquidity: Fixed assets are generally less liquid than financial assets, meaning they can be challenging to sell quickly and convert into cash.
- Environmental Considerations: Investing in fixed assets should be aligned with environmental sustainability, considering factors like energy efficiency and waste management.
Strategic Considerations for Investing in Fixed Assets:
To maximize the benefits of investing in fixed assets, it’s crucial to adopt a strategic approach:
- Thorough Due Diligence: Conduct thorough research and analysis before investing in any fixed asset. Consider factors like location, market demand, and potential for appreciation.
- Diversification: Diversifying your fixed asset portfolio across different asset classes can mitigate risk and enhance returns.
- Financial Planning: Carefully plan your investment strategy, considering your financial goals, risk tolerance, and available capital.
- Professional Advice: Seek professional advice from financial advisors, real estate experts, or other specialists to ensure informed decision-making.
- Long-Term Perspective: Investing in fixed assets is a long-term strategy, requiring patience and a focus on long-term growth and stability.
FAQs about Investing in Fixed Assets:
1. How can I finance the purchase of a fixed asset?
Financing options for fixed assets include:
- Bank Loans: Traditional bank loans offer a structured repayment plan with fixed interest rates.
- Mortgages: Mortgages are specifically designed for financing real estate purchases.
- Leasing: Leasing allows you to use an asset for a specific period without owning it outright.
- Private Equity: Private equity firms can provide capital for large-scale fixed asset investments.
2. How do I determine the fair market value of a fixed asset?
The fair market value of a fixed asset can be determined through:
- Appraisals: Professional appraisers assess the asset’s condition, location, and market demand to estimate its value.
- Comparable Sales: Analyzing recent sales of similar assets can provide insights into market value.
- Income Capitalization: This method estimates value based on the asset’s potential income generation.
3. How can I mitigate the risk of depreciation?
Depreciation is an inevitable part of owning fixed assets. However, you can mitigate its impact by:
- Regular Maintenance: Preventative maintenance and repairs can extend the asset’s lifespan and reduce depreciation.
- Technological Upgrades: Investing in upgrades and enhancements can keep your assets competitive and extend their useful life.
- Strategic Replacement: Replacing aging assets with newer, more efficient models can optimize productivity and minimize depreciation.
4. What are the tax implications of investing in fixed assets?
Tax implications vary depending on your location and specific asset. However, common benefits include:
- Depreciation Deductions: Businesses can deduct depreciation expenses from their taxable income, reducing their tax liability.
- Tax Credits: Governments may offer tax credits for investing in certain types of fixed assets, such as renewable energy or infrastructure projects.
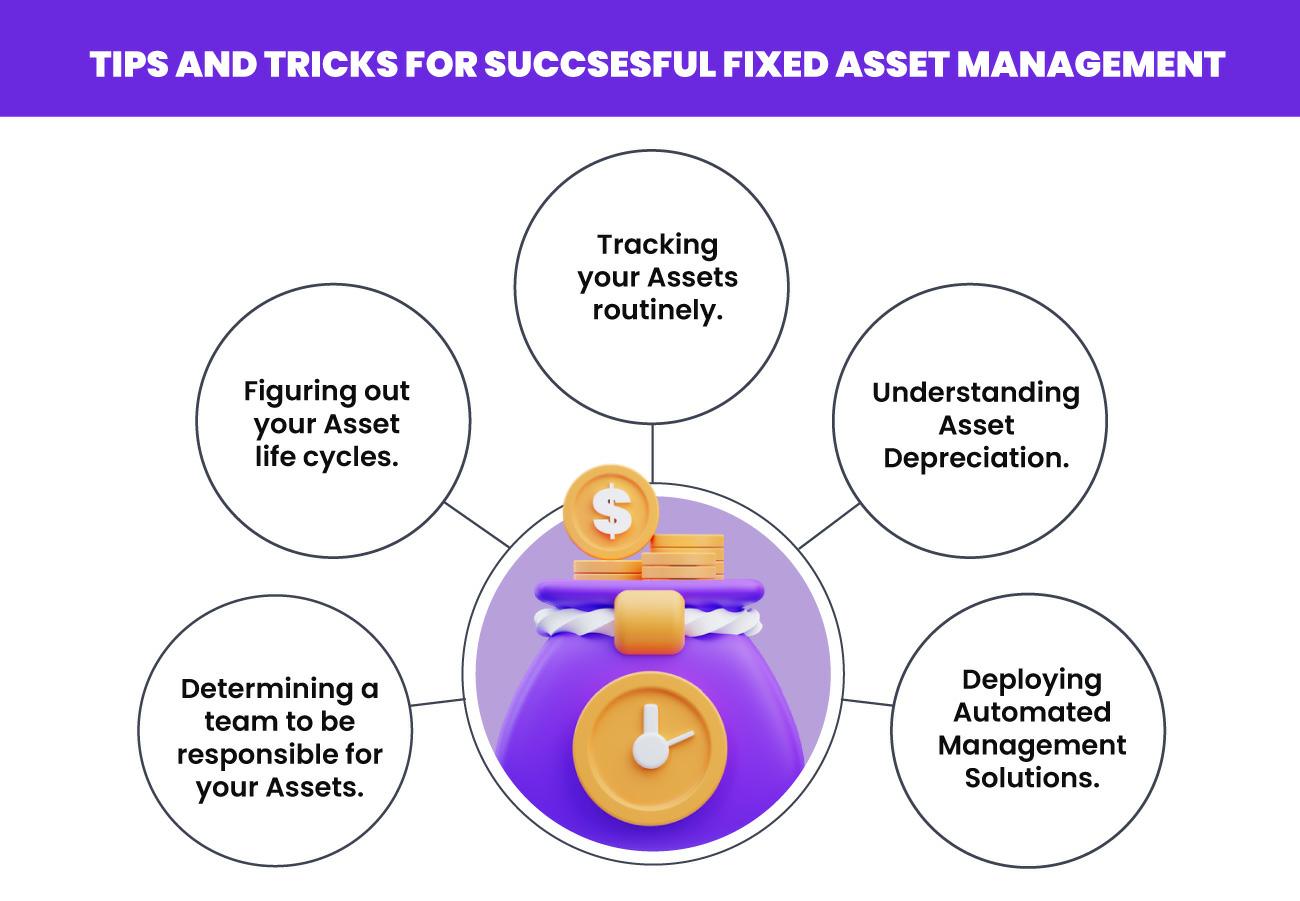
Tips for Investing in Fixed Assets:
- Research Thoroughly: Before investing, conduct comprehensive research on the asset, its potential for appreciation, and the market conditions.
- Assess Your Financial Situation: Carefully evaluate your financial resources, including available capital, debt levels, and cash flow.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consult with financial advisors, real estate experts, or other specialists to gain insights and make informed decisions.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Spread your investments across different asset classes and geographic locations to mitigate risk.
- Monitor Your Investments: Regularly track the performance of your fixed asset investments and make adjustments as needed.
- Consider Long-Term Growth: Focus on long-term value creation and potential for appreciation rather than short-term gains.
Conclusion:
Investing in fixed assets is a strategic approach to building wealth and achieving long-term financial goals. It provides stability, income generation, and the potential for appreciation, making it an essential component of a well-balanced investment portfolio. By carefully considering the advantages, risks, and strategic considerations, individuals, businesses, and governments can leverage the power of fixed assets to create enduring value and secure financial well-being.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Investing in Fixed Assets: A Foundation for Growth and Stability. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!