Understanding the Limitations of ITC Claims: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Limitations of ITC Claims: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Limitations of ITC Claims: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Limitations of ITC Claims: A Comprehensive Guide

The concept of Input Tax Credit (ITC) is a cornerstone of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime in India. It allows registered businesses to claim credit for the taxes paid on inputs used in the production or supply of goods or services. This mechanism helps to reduce the cascading effect of taxes and ensures a smoother flow of goods and services in the economy.
However, there are specific circumstances and situations where ITC cannot be claimed. Understanding these limitations is crucial for businesses to ensure compliance with GST regulations and avoid potential penalties. This comprehensive guide explores the various scenarios where ITC is not permitted, providing insights into the rationale behind these restrictions.
1. ITC on Goods and Services Not Used for Business Purposes:
One fundamental principle governing ITC claims is that the goods or services must be used exclusively for business purposes. Any goods or services acquired for personal consumption or non-business activities are ineligible for ITC. This principle is rooted in the concept of preventing tax evasion and ensuring that the ITC mechanism is used solely for legitimate business transactions.
Examples:
- Purchase of a personal vehicle: A business cannot claim ITC on a vehicle purchased for personal use, even if the vehicle is registered in the business’s name.
- Expenditure on travel and entertainment: Expenses incurred on personal travel or entertainment are not eligible for ITC, even if they are incurred during business trips.
- Household goods: Purchases of household goods like furniture, appliances, or electronics for personal use are not eligible for ITC.
2. ITC on Goods and Services Exempt from GST:
Goods and services that are exempt from GST are not eligible for ITC. This is because the exemption implies that the supplier does not charge GST on the supply, and therefore, no tax credit can be claimed by the recipient.
Examples:
- Supply of agricultural produce: The supply of agricultural produce is generally exempt from GST, and hence, no ITC can be claimed on the purchase of such produce.
- Supply of services by a non-profit organization: Services supplied by a non-profit organization, if exempted from GST, are not eligible for ITC.
- Supply of certain educational services: Certain educational services are exempt from GST, and therefore, ITC cannot be claimed on expenses related to these services.
3. ITC on Goods and Services Supplied by Unregistered Suppliers:
ITC cannot be claimed on goods or services supplied by unregistered suppliers. This restriction is essential to ensure that the GST system is not misused by unregistered entities. When a supplier is not registered under GST, it is assumed that they are not paying GST on their supplies, and therefore, no ITC can be claimed on such purchases.
Examples:
- Purchase of goods from a street vendor: A street vendor is unlikely to be registered under GST, and therefore, no ITC can be claimed on purchases from such vendors.
- Purchase of services from an individual: If an individual is not registered under GST, any services purchased from them are not eligible for ITC.
4. ITC on Goods and Services Used for Making Exempt Supplies:
ITC cannot be claimed on goods and services used for making exempt supplies. This restriction is based on the principle that the exempt supplies are not subject to GST, and therefore, no ITC should be claimed on the inputs used for making these supplies.
Examples:
- Purchase of raw materials for making exempt goods: A business cannot claim ITC on the purchase of raw materials used for making goods that are exempt from GST, such as agricultural produce.
- Purchase of services for making exempt services: A business cannot claim ITC on the purchase of services used for making services that are exempt from GST, such as certain financial services.
5. ITC on Goods and Services Used for Making Zero-Rated Supplies:
While zero-rated supplies are subject to GST, the tax rate is 0%. This means that no GST is payable on these supplies, but the supplier is still required to register under GST. In such cases, ITC can be claimed on the inputs used for making these supplies, but only if the recipient of the zero-rated supplies is a registered person.
Examples:
- Export of goods: Exports of goods are generally zero-rated supplies. A registered exporter can claim ITC on the inputs used for making these exports.
- Supply of goods to SEZs: Supplies of goods to Special Economic Zones (SEZs) are also zero-rated. Registered businesses supplying goods to SEZs can claim ITC on the inputs used for these supplies.
6. ITC on Goods and Services Used for Making Supplies to Unregistered Persons:
ITC cannot be claimed on goods and services used for making supplies to unregistered persons, except for supplies of goods or services that are exempt from GST. This restriction ensures that the ITC mechanism is not used to benefit unregistered entities who are not paying GST on their supplies.
Examples:
- Sale of goods to a consumer: A business cannot claim ITC on the purchase of goods used for making sales to consumers, as consumers are generally not registered under GST.
- Supply of services to an unregistered individual: A business cannot claim ITC on the purchase of services used for making supplies to an unregistered individual.
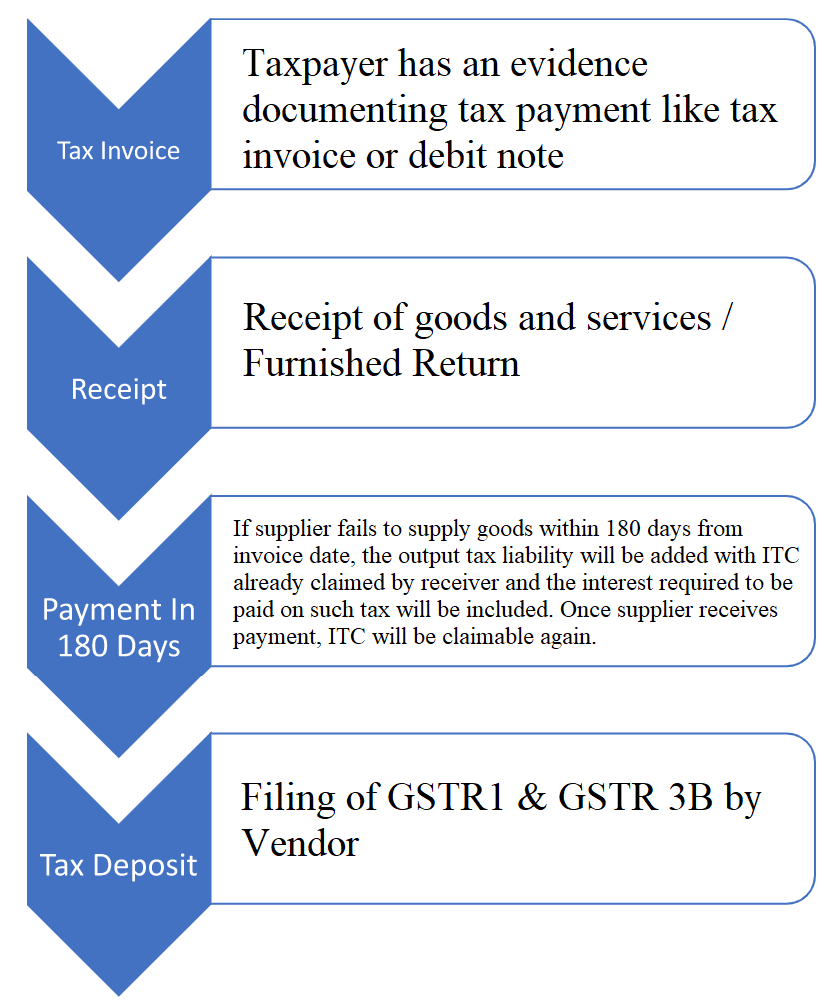
7. ITC on Goods and Services Not Received:
ITC cannot be claimed on goods and services that have not been received. This restriction is based on the principle that ITC can only be claimed for goods and services that have been actually used in the business.
Examples:
- Goods ordered but not yet received: A business cannot claim ITC on goods that have been ordered but not yet received.
- Services contracted but not yet rendered: A business cannot claim ITC on services that have been contracted but not yet rendered.
8. ITC on Goods and Services Not Used Within the Specified Time Limit:
There are certain time limits within which goods or services must be used for business purposes to be eligible for ITC. This time limit varies depending on the nature of the goods or services. If the goods or services are not used within the specified time limit, ITC cannot be claimed.
Examples:
- Capital goods: The time limit for claiming ITC on capital goods is generally five years from the date of purchase.
- Services: The time limit for claiming ITC on services is generally six months from the date of receipt.
9. ITC on Goods and Services Not Supported by Valid Tax Invoices:
ITC can only be claimed if the business has valid tax invoices for the goods or services purchased. The tax invoice must contain all the necessary details, such as the GSTIN of the supplier, the date of supply, the description of the goods or services, and the amount of GST charged.
Examples:
- Missing GSTIN on the tax invoice: If the GSTIN of the supplier is missing on the tax invoice, ITC cannot be claimed.
- Incorrect description of goods or services: If the description of the goods or services on the tax invoice is incorrect, ITC cannot be claimed.
10. ITC on Goods and Services Received from Related Parties:
ITC on goods and services received from related parties can be claimed, but only if certain conditions are met. These conditions include the requirement for the related party to be registered under GST, the supply to be made at arm’s length, and the tax invoice to be issued in accordance with the GST regulations.
Examples:
- Supplies between a parent company and a subsidiary: If a parent company supplies goods or services to its subsidiary, ITC can be claimed by the subsidiary, but only if the conditions mentioned above are met.
- Supplies between two partners in a partnership firm: If two partners in a partnership firm supply goods or services to each other, ITC can be claimed by the recipient partner, but only if the conditions mentioned above are met.
Importance of Understanding ITC Limitations:
Understanding the limitations of ITC claims is essential for businesses to ensure compliance with GST regulations. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in penalties and interest charges. Furthermore, claiming ITC on ineligible goods or services can lead to the rejection of ITC claims and potential audits by the tax authorities.
Benefits of Understanding ITC Limitations:
- Avoid penalties and interest charges: By understanding the limitations of ITC claims, businesses can avoid penalties and interest charges for non-compliance with GST regulations.
- Accurate GST compliance: Understanding the limitations of ITC claims helps businesses to ensure accurate GST compliance and avoid potential audits by the tax authorities.
- Optimize business operations: By understanding the limitations of ITC claims, businesses can optimize their business operations by ensuring that they are only claiming ITC on eligible goods and services.
- Improved financial planning: Understanding the limitations of ITC claims helps businesses to plan their finances accurately and avoid unexpected expenses related to GST compliance.
FAQs on ITC Claims:
1. What is the time limit for claiming ITC on capital goods?
The time limit for claiming ITC on capital goods is generally five years from the date of purchase.
2. Can ITC be claimed on goods or services used for making exempt supplies?
No, ITC cannot be claimed on goods or services used for making exempt supplies.
3. What happens if a business claims ITC on ineligible goods or services?
If a business claims ITC on ineligible goods or services, the tax authorities may reject the ITC claim and conduct an audit.
4. What are the consequences of non-compliance with GST regulations related to ITC claims?
Non-compliance with GST regulations related to ITC claims can result in penalties and interest charges.
5. How can a business ensure accurate GST compliance related to ITC claims?
Businesses can ensure accurate GST compliance related to ITC claims by understanding the limitations of ITC claims, maintaining proper records of all transactions, and seeking professional advice from qualified tax consultants.
Tips for Managing ITC Claims:
- Maintain proper records: Businesses should maintain proper records of all purchases, including tax invoices, to support their ITC claims.
- Seek professional advice: Businesses should seek professional advice from qualified tax consultants to ensure compliance with GST regulations related to ITC claims.
- Stay updated on GST regulations: Businesses should stay updated on GST regulations and any changes that may affect their ITC claims.
- Regularly review ITC claims: Businesses should regularly review their ITC claims to ensure that they are claiming ITC on eligible goods and services.
- File GST returns on time: Businesses should file their GST returns on time to avoid penalties.
Conclusion:
Understanding the limitations of ITC claims is crucial for businesses operating under the GST regime in India. By adhering to these regulations, businesses can ensure accurate GST compliance, avoid penalties, and optimize their business operations. This comprehensive guide has provided insights into the various scenarios where ITC is not permitted, highlighting the importance of staying informed and compliant with GST regulations. By following the tips and advice outlined in this guide, businesses can effectively manage their ITC claims and ensure a smooth and compliant GST journey.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Limitations of ITC Claims: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!