Understanding the Relationship Between Investments and Fixed Assets: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Relationship Between Investments and Fixed Assets: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Relationship Between Investments and Fixed Assets: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Relationship Between Investments and Fixed Assets: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Relationship Between Investments and Fixed Assets: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Defining the Terms: Investments and Fixed Assets
- 3.2 The Interplay Between Investments and Fixed Assets
- 3.3 Analyzing the Relationship: A Case Study
- 3.4 Importance of Understanding the Relationship
- 3.5 FAQs Regarding Investments and Fixed Assets
- 3.6 Tips for Managing Investments and Fixed Assets
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Relationship Between Investments and Fixed Assets: A Comprehensive Guide

The world of finance often presents a complex landscape, riddled with terminology that can seem daunting to the uninitiated. One such concept, frequently encountered in financial discussions, is the relationship between investments and fixed assets. While these terms are often used interchangeably, understanding their distinct characteristics and the nuances of their connection is crucial for informed financial decision-making.
This comprehensive guide aims to demystify this relationship, providing a clear and concise explanation of the fundamental differences between investments and fixed assets, their respective roles within a business and an individual’s financial portfolio, and the intricate ways in which they can be intertwined.
Defining the Terms: Investments and Fixed Assets
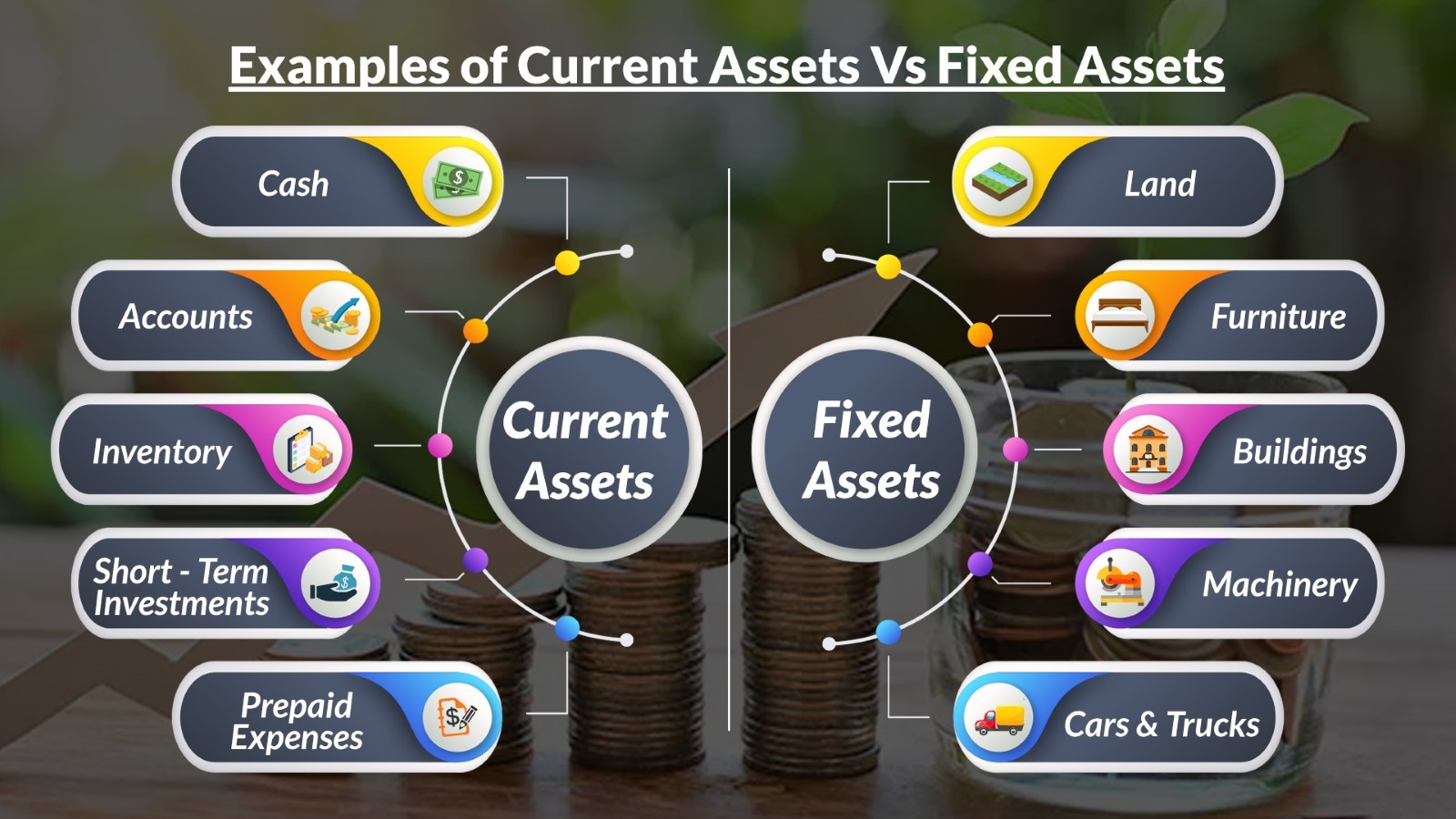
Investments represent financial assets acquired with the expectation of generating future income or appreciation in value. These assets are typically held for a medium to long-term period, with the potential for both gains and losses. Investments can take various forms, including:
- Stocks: Represent ownership in a company, providing shareholders with voting rights and potential dividends.
- Bonds: Debt securities issued by corporations or governments, promising to pay back the principal amount with interest over a specific period.
- Mutual Funds: Pooled investments managed by professionals, offering diversification across various asset classes.
- Real Estate: Tangible assets like land and buildings, potentially generating rental income or capital appreciation.
- Commodities: Raw materials like gold, oil, or agricultural products, often used as a hedge against inflation.
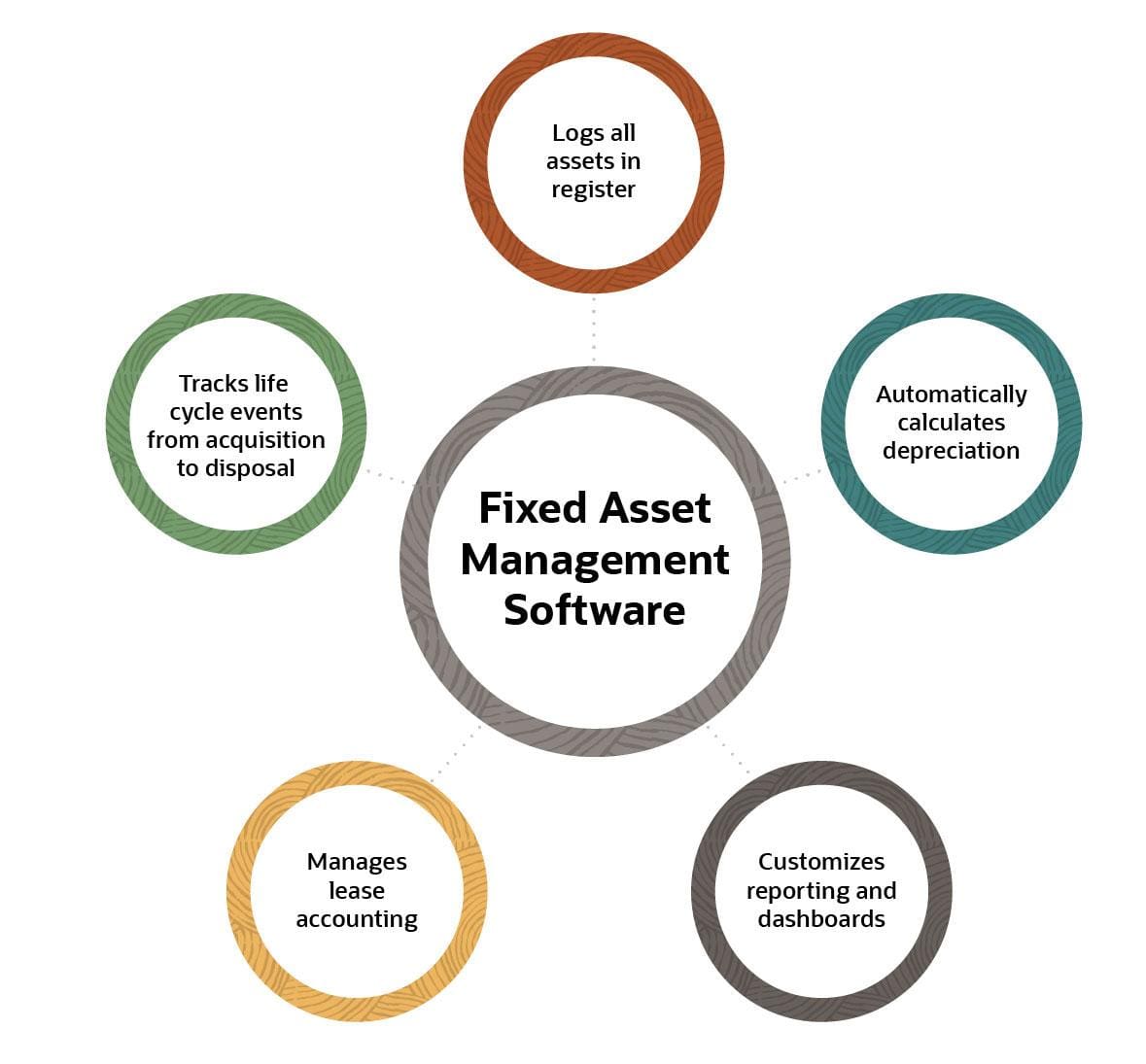
Fixed assets, on the other hand, are tangible assets used in the operations of a business, expected to provide benefits over a long period. These assets are typically categorized as:
- Property, Plant, and Equipment (PP&E): This includes land, buildings, machinery, vehicles, and other physical assets used in production or service delivery.
- Intangible Assets: These assets lack physical form but hold significant value, such as patents, trademarks, copyrights, and goodwill.
The Interplay Between Investments and Fixed Assets
While investments and fixed assets represent distinct categories, their relationship is multifaceted and crucial for understanding financial strategies. Here’s a breakdown of their interconnectedness:
1. Investments Funding Fixed Assets:
A common scenario involves businesses utilizing investments to finance the acquisition of fixed assets. For instance, a company might issue bonds to raise capital for constructing a new factory or purchasing machinery. These investments, in the form of debt financing, provide the necessary funds for acquiring assets that contribute to the company’s operational capacity.
2. Fixed Assets Generating Investment Returns:
Fixed assets can also become the source of investment returns. For example, a company might lease out its excess office space, generating rental income. This income, derived from a fixed asset, can then be reinvested in other ventures, contributing to further growth and expansion.
3. Investments Enhancing Fixed Asset Value:
Investments can directly impact the value of fixed assets. Consider a company investing in research and development, leading to the creation of a new, patented technology. This investment, while intangible in nature, directly enhances the value of the company’s intellectual property, a fixed asset.
4. Fixed Assets as Collateral for Investments:
Fixed assets can serve as collateral for securing loans, which can then be used for making investments. For instance, a business might use its factory building as collateral to obtain a loan for expanding its operations or acquiring new equipment.
5. Investment Returns Funding Fixed Asset Maintenance:
Investments can be utilized to maintain and improve fixed assets. For instance, a company might generate profits from its stock investments, which can be used to fund routine repairs, upgrades, or expansions of its existing equipment.
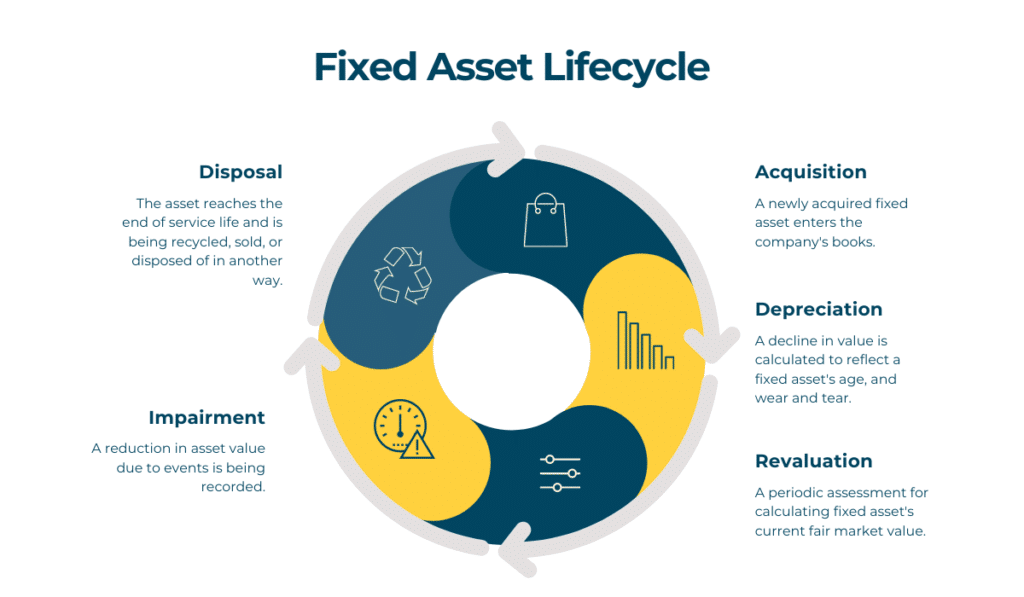
6. Fixed Asset Depreciation and Investment Opportunities:
Fixed assets depreciate over time, which can create investment opportunities. As an asset loses value, businesses might choose to replace it with a newer, more efficient model, potentially funded through investments. This cycle of depreciation and replacement can drive innovation and growth.
Analyzing the Relationship: A Case Study
Imagine a technology startup developing a new software application. This company needs to invest in several fixed assets, including:
- Computer hardware: Powerful servers and workstations are essential for developing and testing the software.
- Software licenses: Specialized tools and development platforms are required for efficient coding and debugging.
- Office space: A comfortable and functional workspace is needed for the team to collaborate and focus.
These investments, while crucial for the company’s operations, are not directly generating revenue. However, they are essential for creating the product that will eventually generate income. The company might finance these investments through:
- Venture capital funding: Investors provide capital in exchange for equity in the company, hoping for future returns.
- Bank loans: The company might secure a loan against its intellectual property, using its software as collateral.
Once the software is developed and launched, it becomes a valuable asset for the company. This intangible asset can be monetized through various means:
- Software licensing: Selling licenses to other companies for using the software.
- Subscription model: Providing access to the software through a recurring subscription fee.
- Acquisition by a larger company: The startup might be acquired by a bigger player, recognizing the value of its software.
In this case study, we see how investments in fixed assets, while not immediately generating revenue, are crucial for building a foundation for future income generation. The success of the software, the company’s intangible asset, depends heavily on the initial investments in tangible assets.
Importance of Understanding the Relationship
Understanding the intricate interplay between investments and fixed assets is vital for both individuals and businesses:
- For individuals: Recognizing how investments can be used to acquire or improve fixed assets, like homes or vehicles, can help in making informed financial decisions.
- For businesses: Understanding how investments can fund fixed asset acquisitions, how fixed assets can generate investment returns, and how depreciation can create investment opportunities is crucial for strategic planning, growth, and profitability.
FAQs Regarding Investments and Fixed Assets
1. Can investments be considered fixed assets?
While investments can be used to acquire fixed assets, they are not considered fixed assets themselves. Investments are financial assets held for future income or appreciation, while fixed assets are tangible assets used in operations.
2. Are all fixed assets acquired through investments?
Not necessarily. Fixed assets can be acquired through various means, including:
- Cash purchases: Businesses might use their own cash reserves to buy fixed assets.
- Debt financing: Loans can be secured for purchasing fixed assets.
- Leasing: Businesses might lease fixed assets, avoiding outright purchase.
3. How do I decide between investing in fixed assets or financial assets?
The decision depends on individual circumstances and goals. Consider:
- Risk tolerance: Investments in financial assets generally carry higher risk but also potential for higher returns.
- Time horizon: Fixed assets are typically held for longer periods, while investments can be more flexible.
- Financial goals: Are you seeking immediate income generation or long-term capital appreciation?
4. What are the tax implications of investing in fixed assets?
Fixed assets are subject to depreciation, which can be deducted as an expense for tax purposes. This reduces taxable income and ultimately lowers tax liabilities.
5. How do I manage the depreciation of fixed assets?
Regular maintenance, upgrades, and potentially replacing aging assets can help mitigate depreciation and prolong the useful life of fixed assets.
Tips for Managing Investments and Fixed Assets
- Diversify your portfolio: Spread your investments across different asset classes to mitigate risk.
- Develop a financial plan: Set clear goals and strategies for managing your investments and fixed assets.
- Seek professional advice: Consult with financial advisors for personalized guidance on investment and asset management.
- Monitor your investments: Regularly review your portfolio and make adjustments as needed.
- Stay informed: Keep abreast of market trends and economic conditions to make informed decisions.
Conclusion
The relationship between investments and fixed assets is intricate and dynamic, requiring a nuanced understanding for effective financial management. While these categories represent distinct asset classes, their interplay is essential for achieving financial goals, whether for individuals or businesses. By comprehending the ways in which investments can be used to acquire, enhance, or maintain fixed assets, and how fixed assets can generate investment returns, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions that contribute to long-term financial success.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Relationship Between Investments and Fixed Assets: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!